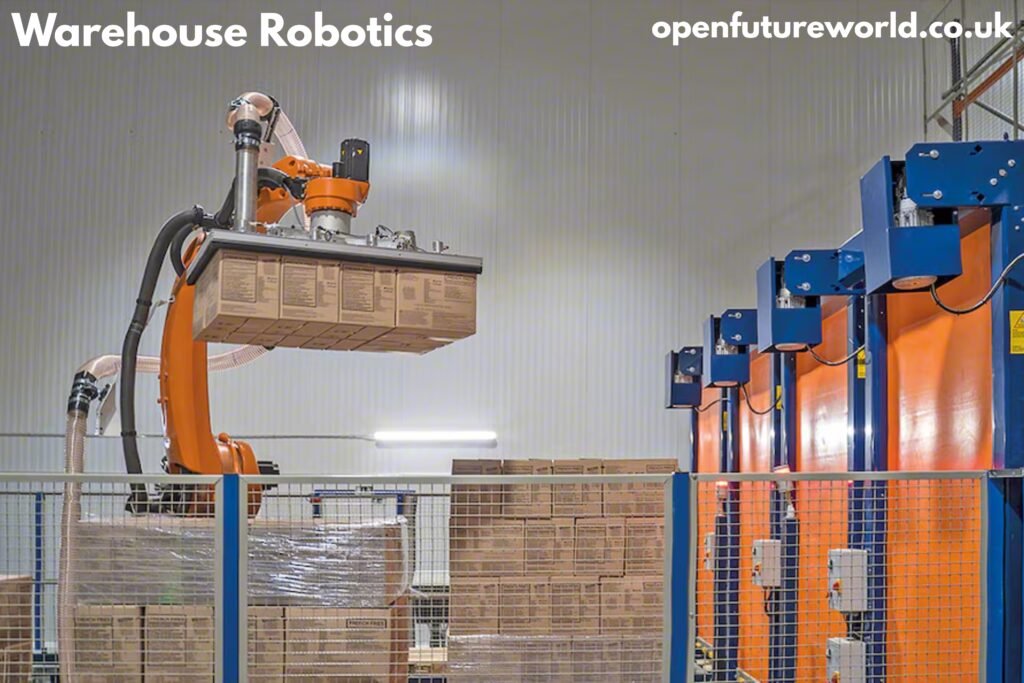
Warehouse Robotics
Warehousing is no longer just about shelves, forklifts, and manual labor. As global supply chains grow more complex and customer expectations rise, businesses are turning to warehouse robotics to stay competitive. From autonomous mobile robots to robotic picking systems, automation is reshaping how goods are stored, moved, and shipped.
Warehouse robotics is not a futuristic concept anymore. It is a practical, proven solution already delivering measurable gains in efficiency, accuracy, and cost control across industries such as e-commerce, manufacturing, retail, and third-party logistics. This article explores what warehouse robotics is, how it works, why it matters, and how organizations can adopt it successfully.
What Is Warehouse Robotics?
Warehouse robotics refers to the use of automated machines, powered by software, sensors, and artificial intelligence, to perform tasks traditionally handled by human workers in a warehouse environment. These tasks include transporting goods, picking and packing orders, sorting items, palletizing loads, and managing inventory.
Unlike traditional automation systems that rely on fixed conveyors and rigid layouts, modern warehouse robots are flexible and adaptive. They can navigate dynamic spaces, collaborate with human workers, and adjust to changing workflows in real time.
At its core, warehouse robotics aims to increase productivity while reducing errors, labor strain, and operational bottlenecks.
Why Warehouse Robotics Is Growing So Fast
The rapid adoption of warehouse robotics is driven by several converging factors that affect businesses worldwide.
Rising E-commerce Demand
Online shopping has dramatically increased order volumes and shortened delivery expectations. Same-day and next-day delivery require faster order fulfillment, which manual operations struggle to achieve consistently.
Labor Shortages and Costs
Many regions face persistent warehouse labor shortages, high turnover rates, and rising wages. Robotics helps fill labor gaps and allows human workers to focus on higher-value tasks.
Need for Accuracy and Speed
Errors in picking and shipping can be costly. Robots reduce mistakes by following precise instructions and integrating with warehouse management systems.
Advances in Technology
Improvements in artificial intelligence, machine vision, sensors, and cloud computing have made warehouse robots more capable, affordable, and easier to deploy.
Key Types of Warehouse Robots
Warehouse robotics is not a single solution. It includes a range of robotic systems designed for specific tasks.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs move goods around the warehouse without fixed paths. They use sensors and mapping technology to navigate safely around people and obstacles. These robots are commonly used for transporting totes, shelves, or pallets between workstations.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs follow predefined routes using markers, wires, or magnetic strips. While less flexible than AMRs, they are reliable for repetitive transport tasks in structured environments.
Robotic Picking Systems
Robotic arms equipped with vision systems can identify, pick, and place items of varying shapes and sizes. These systems are increasingly used in goods-to-person picking and piece picking operations.
Sorting Robots
Sorting robots quickly identify and route items to the correct destination, improving throughput in distribution centers handling high order volumes.
Palletizing and Depalletizing Robots
These robots stack or unstack goods on pallets with speed and precision, reducing physical strain and injury risk for workers.
How Warehouse Robotics Works in Practice
A modern robotic warehouse relies on tight integration between hardware and software. Robots are typically connected to a warehouse management system that assigns tasks, tracks inventory, and optimizes workflows.
For example, when an order is placed, the system directs robots to retrieve items from storage locations and deliver them to a packing station. Sensors and cameras help robots identify items, avoid collisions, and adjust routes. Data collected during operations is analyzed to improve performance over time.
This combination of automation and intelligence allows warehouses to operate with greater consistency and predictability.
Benefits of Warehouse Robotics
The advantages of warehouse robotics go beyond simple automation. Businesses often experience improvements across multiple performance metrics.
- Increased order fulfillment speed and throughput
- Higher picking and inventory accuracy
- Reduced labor dependency and training time
- Improved worker safety and ergonomics
- Better space utilization through optimized layouts
- Scalable operations that adapt to seasonal demand
According to industry data, warehouses that implement robotics can see productivity gains of 20 to 40 percent, depending on the use case and level of automation.
Real-Life Examples of Warehouse Robotics in Action
Many leading companies have already demonstrated the value of warehouse robotics.
Large e-commerce fulfillment centers use fleets of mobile robots to bring shelves directly to workers, reducing walking time and increasing pick rates. Grocery distribution centers rely on robotic picking systems to handle thousands of orders daily with high accuracy. Manufacturers use robotic palletizers to maintain consistent output while minimizing workplace injuries.
Even small and mid-sized warehouses are adopting modular robotic solutions that can be deployed quickly without major infrastructure changes.
Human Workers and Robots Working Together
A common misconception is that warehouse robotics replaces human workers entirely. In reality, most successful deployments focus on collaboration.
Robots handle repetitive, physically demanding, or time-sensitive tasks, while humans manage quality control, exception handling, and decision-making. This approach improves job satisfaction and reduces fatigue.
Warehouses that invest in training and change management often see smoother adoption and stronger employee acceptance of robotic systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While warehouse robotics offers clear benefits, it also comes with challenges that businesses must plan for.
Initial Investment
Robotic systems require upfront capital, including hardware, software, and integration costs. However, many companies achieve a return on investment within two to three years through labor savings and productivity gains.
System Integration
Robots must work seamlessly with existing warehouse management and enterprise systems. Poor integration can limit effectiveness.
Change Management
Introducing robotics changes workflows and job roles. Clear communication, training, and employee involvement are critical for success.
Scalability and Flexibility
Choosing the right solution means considering future growth, product mix changes, and evolving customer demands.
The Role of Data and Artificial Intelligence
Data is a major driver of value in warehouse robotics. Every movement, scan, and task generates information that can be analyzed to improve operations.
Artificial intelligence enables robots to learn from patterns, optimize routes, and adapt to new products or layouts. Predictive analytics helps warehouse managers anticipate demand spikes and adjust resources proactively.
As AI capabilities advance, warehouse robotics will become even more autonomous and efficient.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Warehouse robotics also contributes to sustainability goals. Robots operate with precision, reducing waste from errors and returns. Optimized routes and efficient movement lower energy consumption. Some systems are designed to operate in low-light environments, further reducing power usage.
For companies focused on environmental responsibility, robotics can support both operational and sustainability objectives.

Future Trends in Warehouse Robotics
The future of warehouse robotics points toward greater intelligence, flexibility, and accessibility.
- Increased use of AI-driven vision and grasping technology
- More affordable, modular robots for small warehouses
- Cloud-based control systems and remote monitoring
- Greater standardization and interoperability between systems
- Expanded use of robotics in cold storage and specialized environments
As technology matures, warehouse robotics will become a standard component of modern logistics rather than a competitive advantage reserved for large players.
How to Get Started with Warehouse Robotics
For organizations considering warehouse robotics, a phased approach often works best.
Start by identifying pain points such as slow picking, labor shortages, or high error rates. Evaluate processes that are repetitive and predictable. Pilot a solution in a limited area, measure results, and scale gradually.
Partnering with experienced vendors and involving operations teams early can significantly increase the chances of success.
Conclusion: Why Warehouse Robotics Is a Strategic Investment
Warehouse robotics is transforming how goods move from storage to customer. By combining automation, intelligence, and data, robotic systems help warehouses operate faster, safer, and more efficiently in an increasingly demanding market.
As customer expectations continue to rise and labor challenges persist, investing in warehouse robotics is no longer just an option. It is a strategic step toward building a resilient, scalable, and future-ready supply chain.
If your organization is looking to improve fulfillment speed, accuracy, and operational stability, now is the time to explore how warehouse robotics can fit into your long-term growth strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Warehouse Robotics
What is the main purpose of warehouse robotics?
The main purpose of warehouse robotics is to automate repetitive and labor-intensive tasks to improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in warehouse operations.
Are warehouse robots suitable for small businesses?
Yes, many modern warehouse robotics solutions are modular and scalable, making them suitable for small and mid-sized warehouses with limited space and budgets.
Do warehouse robots replace human workers?
Warehouse robots typically work alongside humans. They handle repetitive tasks while people focus on supervision, quality control, and problem-solving.
How long does it take to see ROI from warehouse robotics?
Most businesses see a return on investment within two to three years, depending on labor savings, productivity improvements, and order volume.
What industries benefit most from warehouse robotics?
E-commerce, retail, manufacturing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and third-party logistics providers all benefit significantly from warehouse robotics.








